
Other forms of storage media are further limited by the speed of the storage bus, such as IDE (PATA), SATA, USB or FireWire. Second, the maximum throughput of a RAM drive is limited by the speed of the RAM, the data bus, and the CPU of the computer. RAM drives can access data with only the address, eliminating this latency. magnetic bubble, acoustic storage, magnetic tape) must move the information to a particular position before reading or writing can occur. A physical hard drive, optical (e.g, CD-ROM, DVD, and Blu-ray) or other media (e.g.
This performance gain is due to multiple factors, including access time, maximum throughput, and file system characteristics.įile access time is greatly reduced since a RAM drive is solid state (no moving parts). The performance of a RAM drive is generally orders of magnitude faster than other forms of digital storage, such as SSD, tape, optical, hard disk, and floppy drives. So RAM devices do offer an advantage to store frequently changing data, like temporary or cached information. Primary memory writes do not so or in far lesser effect. However, solid-state devices do suffer from wear from frequent writing. In the advent of solid-state devices this advantage lost most of its appeal. Historically primary storage based mass storage devices were conceived to bridge the performance gap between internal memory and secondary storage devices. It is sometimes referred to as a virtual RAM drive or software RAM drive to distinguish it from a hardware RAM drive that uses separate hardware containing RAM, which is a type of battery-backed solid-state drive. RAM drives provide high-performance temporary storage for demanding tasks and protect non-volatile storage devices from wearing down, since RAM is not prone to wear from writing, unlike non-volatile flash memory.
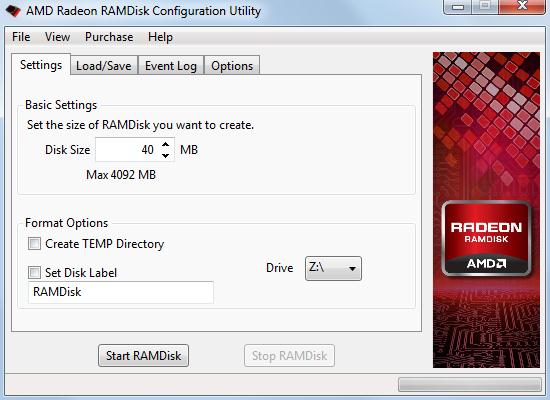
For filesystems without drive emulation, see tmpfs.Ī RAM drive (also called a RAM disk) is a block of random-access memory ( primary storage or volatile memory) that a computer's software is treating as if the memory were a disk drive ( secondary storage). For hardware storage devices using RAM, see solid-state drive. This article is about virtual drives emulated with software.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
